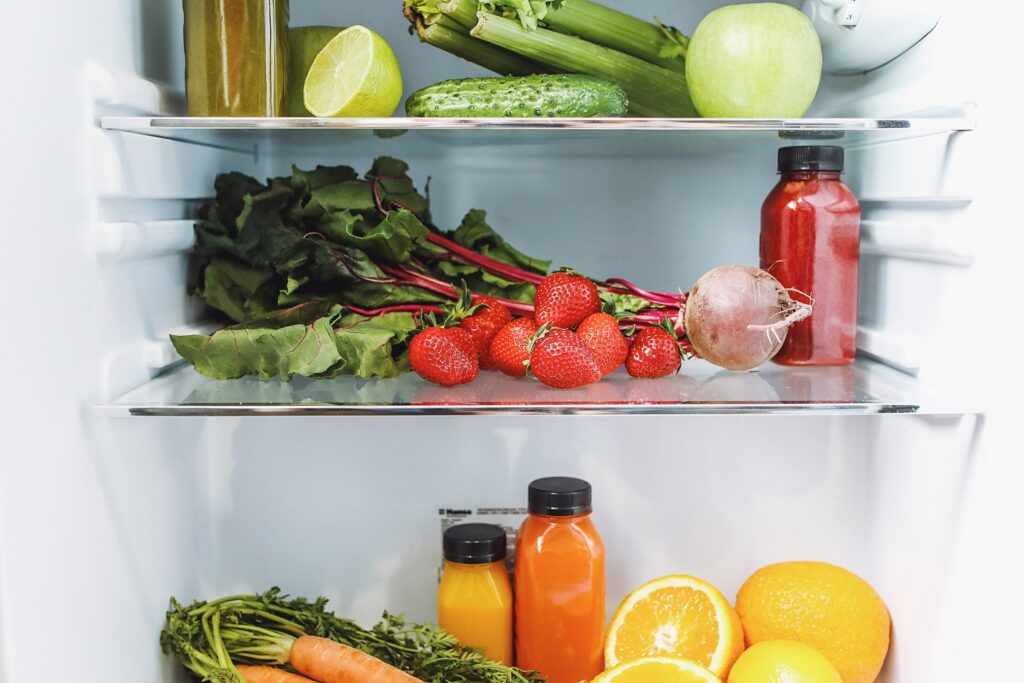
Numerous fruits and vegetables require specific conditions to maintain their freshness. Refrigeration is often the go-to method for ensuring fruit remains in good condition, but you’ll need to know some aspects of refrigeration for the best-tasting food. Read on to learn about the refrigeration of fruits and vegetables and how it may affect your produce purchase.
Fruits in the Refrigerator
Although the cold is a great way of ensuring food remains fresh and prevents spoilage from oxygen exposure, not all fruits should go in your refrigerator. Storing fruits in cold storage will prevent them from ripening properly, leading to poor taste and hardened skin. Continuous exposure to cold will cause most fruits to dry out, but some fruits, such as berries, will need the cold to stay fresh because of how quickly they go bad.
Vegetables in the Refrigerator
You can store most vegetables in the refrigerator since they are highly sensitive to the elements around them. The microorganisms that live on vegetables, such as bacteria, require energy from light, heat, and moisture to stay alive. These microorganisms lead to rot, which can quickly occur when you don’t refrigerate your veggies.
Certain leafy vegetables need specific temperatures and humidity in the air to remain in good condition. Storing and shipping lettuce requires a temperature limit between 40 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit. It’s a safe bet to put most vegetables in the refrigerator, and if you leave some out, avoid keeping them at room temperature for more than a day to prevent bacteria from growing.
What Goes in the Refrigerator?
The defining elements in most cases regarding keeping produce on the kitchen counter are the heat and moisture levels in the air. These elements will cause spoilage because the bacteria will multiply faster and grow stronger, consuming the food’s nutrients and causing it to rot. Food that should go in the refrigerator may include:
- Berries
- Grapes
- Carrots
- Broccoli
- Lettuce
- Spinach
Most leafy vegetables and small soft fruits will preserve better in the fridge; however, you’ll still want to eat them within a few days of storing them for maximum freshness.
What Produce Can I Leave Out?
Produce must ripen to achieve a sweet or savory taste. Bananas are a good example of a food that needs to ripen for the best taste.
If the banana is too green, it will taste bitter and have a firmer texture. As the banana softens in a room temperature setting, it tastes sweeter after a few days. The same process applies to products such as:
- Tomatoes
- Apples
- Potatoes
- Mangoes
- Cucumbers
The only exception is apples; they taste delicious outside or inside the refrigerator, but eating them at room temperature is typically best.
Refrigerating fruits and vegetables is important, but you must consider what each storage option will do to your produce for the best result. Remember this information the next time you visit your local farmers market, and place your produce in the right place for the best taste.
You Might Also Like:
- Ways To Make Eating Vegetables Fun for Everyone
- Natural Ways To Protect Your Vegetable Garden From Pests
- The Wonderful Benefits of Starting a Home Garden With Your Kids
- 3 Reasons Why You Should Purchase Organic Produce

As always, sharing is caring! Please click on the buttons below to share this post with your friends!